Pipe type: seamless pipe, seamless steel pipe, seamless carbon steel pipe, carbon seamless steel pipe,
Standard and Grade: ASTM A106, Grade B; ASTM A53, Gr.A,Gr.B; DN 17175/EN10216-2, Grade ST35, ST45, ST52, 13CrMo44; DIN 2391/EN10305-1, Grade St35, St45, St52; DIN 1629/EN10216-1, Grade St37, St45, St52; JIS G3429 STH11; JIS G3429 STH12; JIS G3429 STH21; JIS G3429 STH22
O.D.: 10mm-720mm
W.T.: 1mm-120mm
Length: 6000mm-12000mm
Application: High Temperature Seamless Carbon Steel Nominal Pipe
Surface: oiled or unoiled
Ends: plain ends, beveled with tube cap
Package: by bundle or bulk
Email:sales@sqsteelpipe.com
Whats App: 008613761124029
Skype:steelproducts
Wechat:137463635
ASTM A106 seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service
ASTM A106 seamless pressure pipe (also known as ASME SA106 pipe) is commonly used in the construction of oil and gas refineries, power plants, petrochemical plants, boilers, and ships where the piping must transport fluids and gases that exhibit higher temperatures and pressure levels.
ASTM A106 Seamless Pressure Pipe (also known as ASME SA106 pipe) covers seamless carbon steel nominal wall pipe for high-temperature service. Suitable for bending, flanging and similar forming operations.
NPS 1-1/2″ and under may be either hot finished or cold drawn. NPS 2″ and larger shall be hot finished unless otherwise specified.
Process
Killed steel, with primary melting process being open-hearth, basic-oxygen, or electric-furnace, possibly combined with separate degassing or refining.
Steel cast in ingots or strand cast is permissible.
Hot-finished pipe need not be heat treated.
Cold-drawn pipe shall be heat treated after the final cold draw pass.
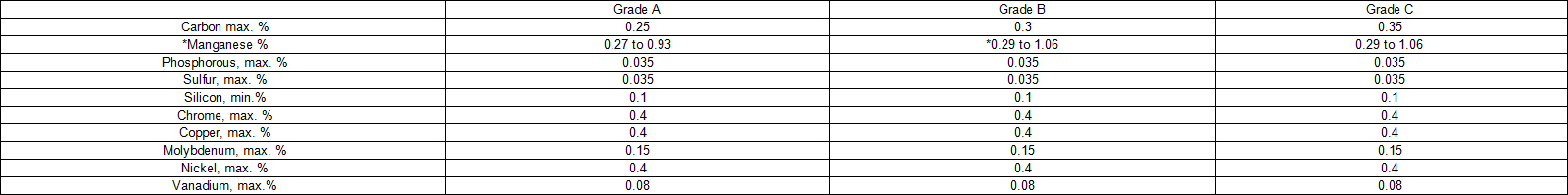
Chemical Requirements
Permissible Variations in Wall Thickness
The minimum wall thickness at any point shall not be more than 12.5% under the nominal wall thickness specified.
Permissible Variations in Weights per Foot
Weight of any length shall not vary more than 10% over and 3.5% under that specified. NOTE — NPS 4 and smaller — weighed in lots. Larger sizes shall be weighed separately by length.
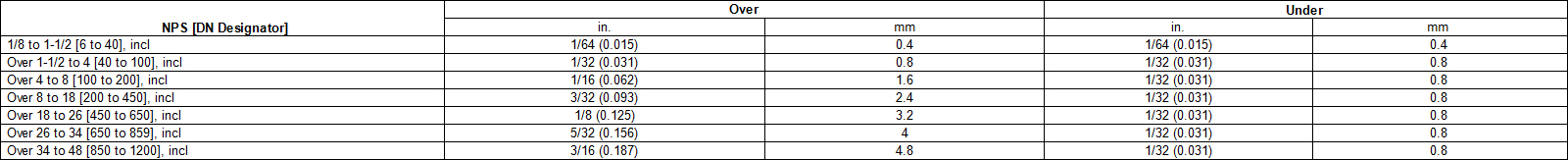
Permissible Variations in Outside Diameter
Outside Diameter at any point shall not vary from standard specified more than:
Tensile Requirements

Number of Tests Required

Hydrostatic Testing
Inspection test pressures produce a stress in the pipe wall equal to 60% of specified minimum yield strength (SMYS) at room temperature. Maximum Pressures are not to exceed 2500 psi for NPS3 and must stay under 2800 psi for the larger sizes. Pressure is maintained for not less than 5 seconds.
Mechanical Tests Specified
Tensile Test — NPS 8 and larger — either transverse or longitudinal acceptable Smaller than NPS 8 — weighed in lots. Larger sizes — by length. Flattening Test — NPS 2-1/2 and larger. Bending Test (Cold) — NPS 2 and under.

Lengths
Lengths required shall be specified on order. No “jointers” permitted unless otherwise specified. If no definite lengths required, following practice applies: Single Random — 17′ ~ 24′ lengths Double Random — 36′ ~ 44′ lengths
Required Markings on Each Length
(On Tags attached to each Bundle in case of Bundled Pipe) Rolled, Stamped, or Stenciled (Mfrs. Option) Manufacturer’s name or brand. Length of pipe. A106 A, A 106 B, A 106 C. ANSI schedule number. Hydrostatic test pressures and/or NDE; Weight per foot (NPS 4 and larger) or NH if neither is specified. Additional “S” if tested supplementary requirements.
*ASTM A 106 grade B Seamless Pressure Pipe
Unless otherwise specified by the purchaser, for each reduction of 0.01 % below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06 % manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a maximum of 1.65 %.
A Seamless steel pipe can be made from any of several alloys and metals such as carbon steel, stainless steel, molybdenum or tungsten.
Some of the differences between Seamless steel pipes and welded tubes are:
※A Seamless steel pipe is extruded and drawn from a billet whereas a welded tube is produced from a strip that is roll formed and welded to produce a tube.
※Since a Seamless steel pipe offers a higher range of safety measures it is more expensive than a welded tube.
※A Seamless steel pipe is relatively short in length, whereas welded tubes can be manufactured in long continuous lengths.
※A Seamless steel pipe generally doesn't show any sign of corrosion until and unless it is subjected to a highly corrosive environment, whereas the weld area in the welded tube is much more prone to corrosion attacks.
※A welded area is considered to be inhomogeneous, thus it exhibits a different malleability and less corrosion resistance as well as greater dimensional variation.
※A Seamless steel pipe eliminates any such issues and thus offers high corrosion resistance.
Characteristics
Seamless steel pipe for the use of engineering and construction is very widely, it is a hollow steel strip no seams, it is mainly used to transport liquids pipelines, different look and general steel,one of those heavy type steel, it has a strong resistance to corrosion, resistant to general corrosion.
※ High precision can do small batch production.
※ Smaller diameter.
※ Weldability strong, high compression capability.
※ Steel pipe superior performance, relatively dense metal.
※ Steel Cross area is more complex.
※ High precision cold drawn products, good surface quality.
Mechanical properties:
The mechanical properties of the seamless steel tube is a important indicator that ensure seamless pipe end-use properties (mechanical properties), which depends on the chemical composition and heat treatment of steel.
In steel standards, according to different requirements, it provide the tensile properties (tensile strength, yield strength or yield point elongation) and hardness.
① Tensile strength (σb)
During stretching, when pull off the bear most strongly (Fb), divided by the original cross-sectional area (So) from the stress (σ), known as the tensile strength (σb), units of N/mm2 (MPa). It said the maximum capacity resist destruction of metallic materials under tension.
② Yield point (σs)
Yield the phenomenon of metal materials, the sample does not increase during the tensile force (remains constant) and continue elongation stress is known as the yield point. If the force drop occurred, you should distinguish between upper and lower yield point. The yield point of the unit is in N/mm2 (MPa). On yield point (σsu):Sample to yield the maximum stress and force the first drop; lower yield point (σsl): yield minimum stress in the stage when excluding the initial transient effect.
③ Elongation (σ)
In the tensile test, the specimen fractured a percentage of the gauge to increase the length of the original gauge length, called elongation. Σ, said the unit is%.
④ Cross-section contraction rate (ψ)
In the tensile test, the percentage of the specimen fractured its shrink the diameter at the cross-sectional area of the maximum reduction and the original cross-sectional area is known as section shrinkage. Ψ expressed in%.
⑤ Hardness testing
Metallic materials against hard objects indentation of the surface, known as hardness. accoring to the test method and scope of application, the hardness can be divided into brinell hardness, Rockwell hardness, Vickers hardness, Shore hardness, hardness and high temperature hardness. Commonly used for pipe, Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers hardness of three kinds.
